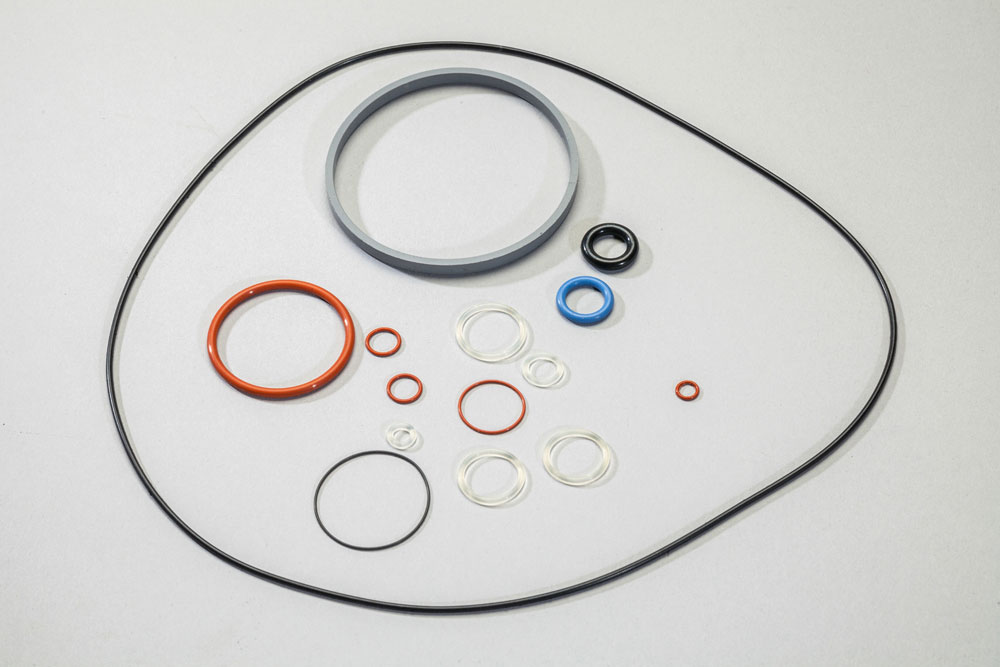
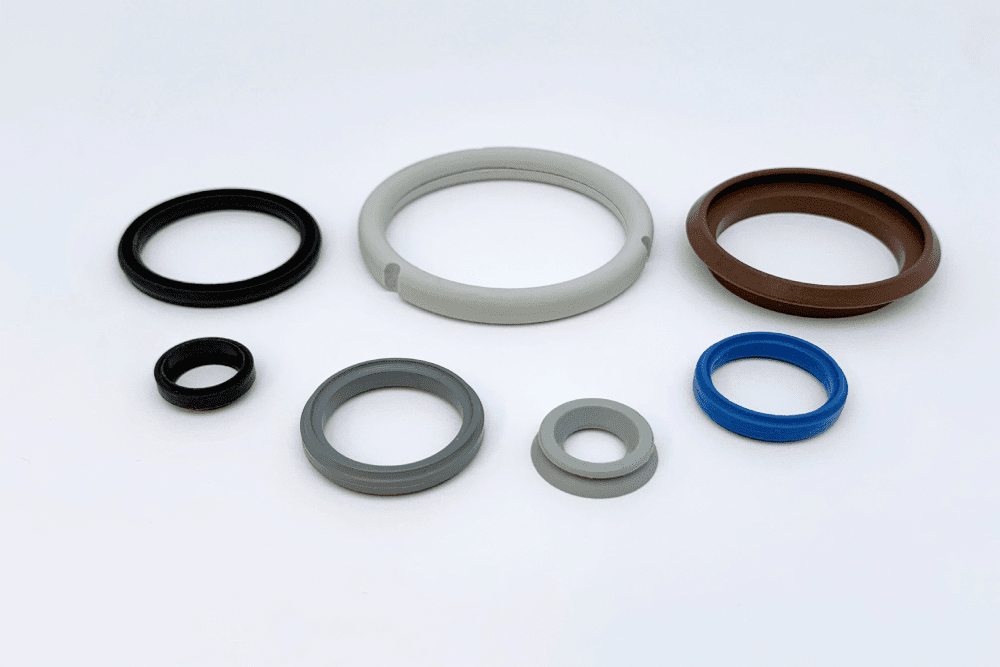
Rubber molded components are incorporated into a wide range of products, applications, and industries from aerospace and defense to medical device equipment. Mission-critical applications require custom rubber molds and tooling to meet customer-specific engineering specifications.
With more than 35 years of experience, RD Rubber Technology Corporation has the knowledge and equipment necessary to create custom-molded components for our customers in many industries. Our extensive custom rubber molding capabilities include compression molding, transfer molding, injection molding, liquid silicone rubber molding, and rubber to metal bonding.
Liquid Injection Molding
Liquid silicone rubber is pumped from different types of containers, varying from sealed tubes to 55-gallon drums, through specialized hoses and tubing to the molding equipment. The two material components (A and B) are pumped through a static mixer by a metering pump. Once the two components are mixed, the curing process begins immediately. A chiller supplying cold water to jacketed fittings is typically used to slow the curing process prior to the materials entering the heated mold. Color pigments can also be added with a color injector together with the material pump before the material enters the static mixer section. In the static mixer, the material components are mixed and transferred to the temperature-controlled metering section of the injection molding machine. This contrasts with high consistency rubber (solid) rubber materials that are purchased pre-mixed and un-vulcanized. The mixed compound is then pushed into a heated cavity to vulcanize the material.
The liquid silicone rubber injection molding process produces rubber molded components with extreme accuracy for outstanding consistency and repeatability. This makes it ideal for manufacturing parts with complex details and exacting geometries. Unlike other rubber molding processing options, liquid injection molding does not require pre-forms, which significantly reduces the amount of time and labor necessary for a full production run.
The comparatively low viscosity of liquid silicone rubber allows the cavity to fill quickly for quicker cycle times, thereby shortening production and reducing overhead. In addition, this method uses the precise amount of material required for each part to minimize waste.
Rubber Compression Molding
Compression molding is a closed mold process frequently used for low to medium production volumes. Example applications include seals, O-rings, gaskets, grommets, valves, diaphragms, poppet assemblies, plungers, latches, flappers, vacuum cups, boot pads, switches, covers, shells, housings, cases, connectors, and buttons. In compression molding, an uncured rubber profile or preform is carefully positioned into a heated mold and then into the compression molding press which subjects the mold to high clamping pressure to fill the mold cavity with the preform material. The rubber conforms to the shape of the mold and is cured to produce a molded component. Compared to injection molding, rubber compression molding offers lower mold costs and quick mold changeovers with longer production cycle times.
Rubber Transfer Molding
Transfer molding begins by measuring the required uncured material and positioning it into the “pot” section of the transfer mold. The transfer mold is then closed and placed into the molding press. The plunger compresses the material as heat is applied and the ensuing pressure transfers the uncured rubber through the runners into the mold cavities to cure the material to the desired shape. The next step involves trimming or deflashing to remove unwanted overflow material or flash. Transfer molding provides precise control of dimensional tolerances. Although pre-formed materials are required, a single pre-form can fill multiple mold cavities.
Transfer molding is more labor efficient compared to compression molding but produces more material waste.
Why Partner With RD Rubber / Made in USA / Build Trust / Local Manufacturer
 At RD Rubber Technology Corporation, we are committed to providing our customers with dependable, trusted rubber manufacturing solutions. Our team of engineers and technicians work to exceed our customers’ expectations by understanding every aspect of your project.
At RD Rubber Technology Corporation, we are committed to providing our customers with dependable, trusted rubber manufacturing solutions. Our team of engineers and technicians work to exceed our customers’ expectations by understanding every aspect of your project.
Using our ISO 9001:2015 and AS 9100:2016 Certified Quality Management System, we rigorously monitor each step of the development and manufacturing process from the initial consultation through inspection and distribution.
We are committed to creating exceptional products through the application of outstanding product development and quality engineering services. Our dedication to quality is reflected in our certifications and registrations, which include:
- ISO 9001:2015 Certified
- AS 9100:2016 Certified
- ITAR Registered
- Military Specifications
- MIL-I-45208A
- ANSI Z540-1
- ISO 10012-1 and ISO 3601-3
- GMP Standards
Contact our experts today to learn more about our custom rubber molding capabilities, or request a quote for pricing on your next project.